AIM:
To write a C++ program for maintaining bank account using constructor overloading.
ALGORITHM:
STEP 1: Start the program.
STEP 2: Declare the data members and constructors.
STEP 3: Define the constructors outside of the class.
STEP 4: Display the bank account details.
STEP 5: Stop the program.
PROGRAM CODE:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class account
{ int acc_no; float bal; public: account(); account(int); account(int,float); account(account &obj); void display() { cout<<"n Account number is :"<<acc_no; cout<<"n Balance is :"<<bal; }
};
account::account()
{ acc_no=413; bal=15.9;
}
account::account(int val)
{ acc_no=val; bal=0.0;
}
account::account(int val1,float val2)
{ acc_no=val1; bal=val2;
}
account::account(account &obj)
{ acc_no=obj.acc_no; bal=obj.bal;
}
void main()
{ clrscr(); account o1; account o2(1030); account o3(1040,1400.5); account o4(o3); account o5=o1; o1.display(); o2.display(); o3.display(); o4.display(); o5.display(); getch();
}
OUTPUT:
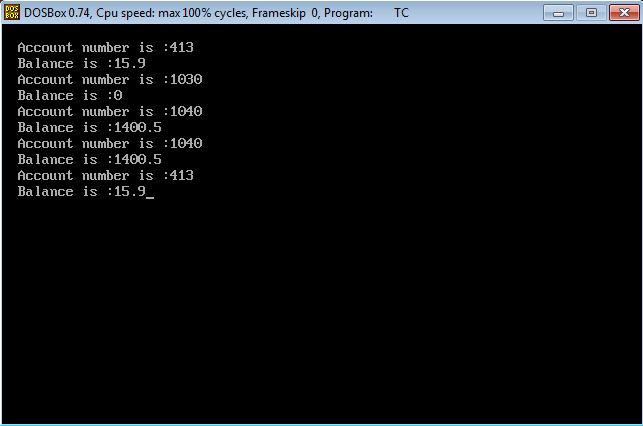
RESULT:
Thus the C++ program for maintaining bank account using constructor overloading is written and executed successfully.


![How to Clear Terminal Screen in Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions [Beginner’s Tip]](https://linuxpunx.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/how-to-clear-terminal-screen-in-ubuntu-and-other-linux-distributions-beginners-tip-768x415.gif)