A Private Cloud is a cloud environment where computing resources are exclusively dedicated to one organization. Although it can be hosted on-premises, it is usually outsourced to a specialized Private Cloud provider.
What is a Private Cloud?
A Private Cloud is a cloud infrastructure where computing resources are exclusively dedicated to one organization. As opposed to the Public Cloud approach, resources are not shared with other customers and, therefore, companies maintain greater control over the performance of their virtualized IT infrastructure.
In the Private Cloud approach, resources are highly protected against any activities performed by neighboring customers, both in security, privacy and performance guarantee terms.
Private Cloud environments are ideal for any type of businesses and projects. Besides, it is the most common cloud deployment model to host mission-critical data and applications in need of high performance, availability and security levels. The Private Cloud services market is expected to grow at a 29.7% CAGR from 2022 to 2029, until reaching $528 billion, according to Maximize Market Research.
How does a Private Cloud work?
A Private Cloud is a single-tenant infrastructure or environment where resources are exclusive to each organization. Servers are occupied by single customers.
Resources can be hosted within the organization’s on-premise data center or hosted by a cloud provider, in an off-site data center. Organizations can either fully manage their environment or partially or fully outsource its management to a managed services provider. Nevertheless, when opting for outsourcing, the Private Cloud provider is responsible for purchasing, managing, monitoring and maintaining the physical infrastructure.
Main Private Cloud benefits
Private Cloud environments offer the flexibility of the cloud while providing a higher level of performance, control, security and privacy.
Organizations opt for a private cloud deployment in order to benefit from the efficiency and service customization inherent to single-tenant environments; as well as to meet regulatory compliance requirements. Using a Private Cloud is similar to having a dedicated data center, while leveraging the advantages of the Cloud. Not only do companies no longer need to maintain their own infrastructure and dedicated servers, but they can also accelerate provisioning and deployment procedures.
Exclusive use of resources
The Private Cloud model offers similar advantages to owning a data center on-premises. When opting for this model, companies do not share their computing resources with other customers. This prevents their performance from being affected by the activity of other virtual machines within the same physical infrastructure. An issue that can happen in public cloud solutions where resources can be oversubscribed.
So, by keeping resources exclusive with a dedicated cloud, companies enjoy predictable performance, free of noisy neighbors.
Transparent and controlled costs
While scalability is important, so is keeping the IT budget under control. Unlike many people think, dedicated cloud environments such as those we design at Stackscale are truly competitive. A Private Cloud environment is often the most suitable choice in terms of cost-efficiency.
Most of the workloads in businesses are predictable and, therefore, it is more cost-efficient to run them in a Private Cloud than in a Public Cloud.
Moreover, thanks to the cloud, companies do not need to do large capital investments in purchasing and upgrading IT equipment and, at the same time, they can reduce management costs. However, the lack of transparency in some public cloud solutions often make cloud costs go through the roof. Cost management issues are actually one of the reasons behind cloud repatriation.
But that is not the case with Private Cloud environments, as costs are usually much easier to control. Compared to the substantial usage fees in public clouds and the costs associated with data center management in on-premise solutions, a private cloud infrastructure provides the best of both worlds. At Stackscale, for instance, we follow a transparent pricing structure and billing policy, so that customers know cloud infrastructure costs beforehand.
Greater control and security
A Private Cloud approach, by nature, considerably reduces the number of expected security threats. Customers enjoy greater security and control over their IT environment, since they do not share their resources with other customers.
Besides, with the right protocols and measures in place, a private cloud offers further compliance and security compared with an on-premise data center. That is why more and more organizations opt for private cloud solutions for those workloads dealing with personally identifiable information, medical records and other sensitive data.
Data protection
Private Cloud makes it easier to meet data protection requirements.
With Private Cloud solutions, customers can easily know the location of their services. Moreover, regarding regulatory compliance, companies should always make sure the provider’s server location complies with their business’ local regulation. For instance, in order to comply with data protection laws in the European Union, it is most recommended to trust in reliable data centers within Europe.
Public Cloud vs Private Cloud
To sum up, here is a table with some of the most common differences between public cloud environments and private cloud environments.
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
| Shared resources. | Dedicated resources. |
| Hosted by a cloud service provider. | Hosted by a cloud service provider or in-house. |
| Connectivity over the public Internet. | Connectivity over the public Internet or over a secure private network. |
| Proprietary standards. | Open standards. |
| Low initial costs. | Controlled costs over time. |
| Requires a high level of security on the company’s behalf. It does not include dedicated proactive monitoring. | Requires a medium level of security on the company’s behalf. It includes dedicated proactive monitoring. |
| Ideal for handling unusual traffic peaks. | Ideal for mission-critical IT workloads and predictable traffic peaks. |
| Low visibility and control into the infrastructure. | High visibility and control into the infrastructure. |
| High scalability. | High scalability when opting for a hosted private cloud. |
| Suitable for non-sensitive information. | Suitable for sensitive data; specially focused on data protection and data sovereignty. |
You can discover more about the differences between the public and private cloud in the post about Stackscale’s Private Cloud vs Public Cloud.
From on-premise Private Cloud to hosted Private Cloud
Private Clouds were traditionally hosted on-premises, within the company’s facilities. However, this approach is becoming less and less common. Why is it so? Because a Private Cloud hosted by a cloud service provider makes it easier to leverage the advantages of the cloud.
- A hosted Private Cloud allows companies to scale more easily.
- Companies do not need to maintain, manage and upgrade their own physical infrastructure.
- The IT team can focus on tasks adding more value to the business.
The adoption of hosted Private Cloud solutions is increasingly popular among organizations. This rise is due to the need of having a dedicated cloud environment without incurring purchase, management, maintenance and upgrading costs. Besides, compared to public cloud platforms, dedicated cloud environments make it easier for companies to integrate their existing services, applications and software. Since Private Cloud environments can be more easily adapted to each customer’s requirements.
How is private cloud different from on-premise
Increased productivity, a shorter time-to-market and cost optimization are some of the benefits of having a private cloud. Here is a table comparing the main differences between a private cloud environment and an on-premise data center.
| Private cloud | On-premise |
| OPEX model. | CAPEX model. |
| OPEX savings thanks to outsourcing management and maintenance. | High operational expenditure related to data center management and maintenance, and recruitment. |
| High scalability. | Low scalability. |
| High-Availability at a competitive price. | High-Availability is more expensive to achieve. |
| Affordable 24/7 support and monitoring. | Costly 24/7 support and monitoring. |
| Affordable and competitive business continuity and disaster recovery, thanks to a greater level of security and redundancy. | Achieving the same level of business continuity and disaster recovery is harder and less cost-efficient. |
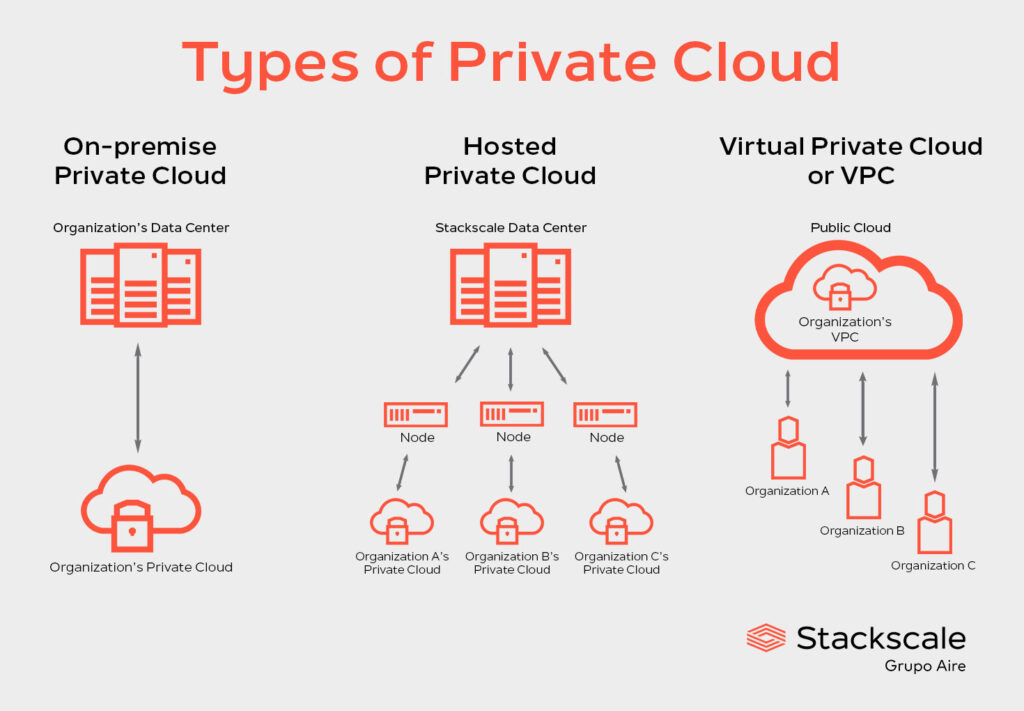
Types of Private Cloud
There are different types of private cloud that offer different advantages to businesses:
- On-premise Private Cloud. This type of Private Cloud consists of creating a private, virtualized environment within the organization’s on-premise data center.
- Hosted Private Cloud. This type of Private Cloud offers dedicated resources to organizations, delivered by a third-party provider such as Stackscale. Servers continue to be exclusive to each organization and independent from the activities of other customers.
- Virtual Private Cloud or VPC. This type of Private Cloud uses an isolated environment within a Public Cloud. This allows organizations to run their workloads using private resources but the servers continue to be shared with other customers.
To sum up, among the different types of cloud, hosted Private Cloud environments stand out for offering dedicated resources at the best high-performance, security and control ratio. If you are looking for a secure, reliable and cost-efficient cloud solution for your mission critical applications, do not hesitate to contact our experts for a custom quote.