In this post we want to collect the most common terms in cloud computing; from basic concepts such as the main cloud service models and types of cloud to more specialized concepts related to cloud computing. Let’s start from the beginning…
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is a computing resources and services distribution model —from applications to storage resources, networking and processing capabilities— over the Internet, on demand and on a pay per use model. So, in cloud computing, cloud providers or ISPs are responsible for managing computing resources and applications, depending on the cloud service model they offer. While users only pay for the services they use and scale whenever they need. Although the term “cloud computing” started to gain popularity at the beginning of the 21st century, the concept “computing as a service” was already known as “virtualization” before.
Cloud computing glossary
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A
API
An API, short for Application Programming Interface, is a set of definitions and protocols used to develop and integrate software of applications. It enables software applications to communicate between them using a collection of rules.
B
Backup
A backup is a copy of data that is taken and stored somewhere else so that, in case of a data loss incident, data can be recovered and restored. It is a simple form of Disaster Recovery.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the maximum data transfer capability of a network or Internet connection; that is to say, the amount of data that can be sent through a connection at the same time. Bandwidth is usually measured in Megabits per second (Mbps).
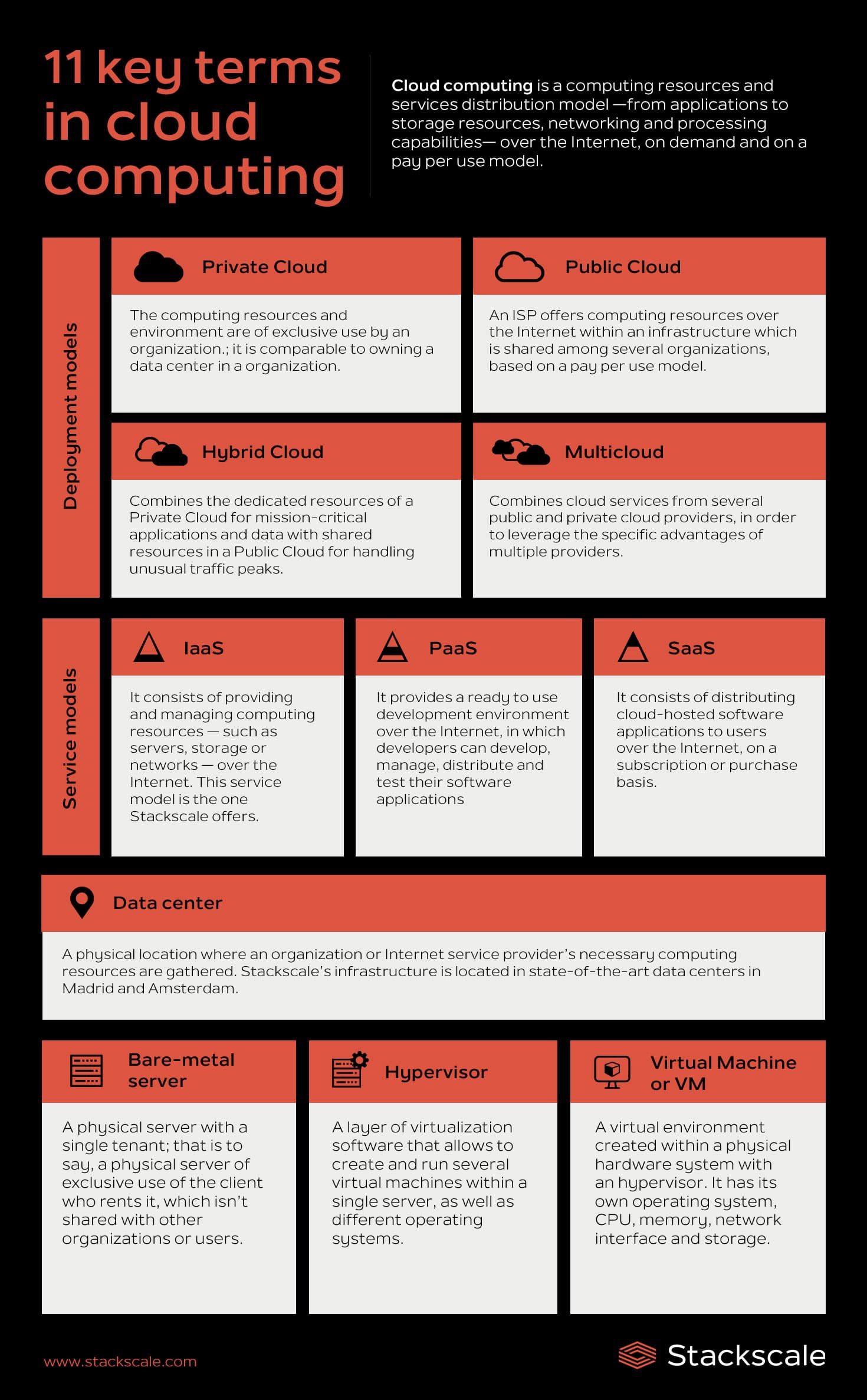
Bare-metal server
A Bare-metal server is a physical server with a single tenant; that is to say, a physical server of exclusive use of the client who rents it, which is not shared with other organizations or users. Single-tenant, bare-metal servers outperform traditional on-premise and public cloud solutions.
C
CAPEX
CAPEX, short for Capital Expenditure, refers to the amount of money a company spends on acquiring and upgrading goods. These can be either tangible, like hardware and facilities, or intangible, like software licenses and intellectual property. Learn more about CAPEX in this post about cloud costs.
CDN
A CDN or Content Delivery Network is a network of servers and data centers which are geographically distributed in order to improve availability and performance by placing content copies in a cache closer to end users. More details aboutwhat a CDN is.
Cluster
A cluster is a group of servers that are connected with each other over a network, and which acts as a single server in many aspects.
Cloud migration
Cloud migration is the process of transferring, partially or completely, a company’s data, applications and services from an on-premise solution to a cloud environment. Discover some key elements to prepare a secure migration to the cloud.
Cloud native
The term cloud native is used to describe applications that have been designed and built to fully leverage the benefits of the cloud model — scalability, elasticity, resilience and flexibility.
Cloud repatriation
Cloud repatriation, also known as “uncloud”, refers to the relocation of workloads and applications from hyperscale public clouds to other IT solutions — hosted private cloud environments, colocation facilities, dedicated servers or even smaller public cloud environments. More details aboutcloud repatriation.
Colocation
Colocation facilities are a type of data center where companies can rent space, power, bandwidth, cooling and physical security to host their IT equipment. Colocation centers also offer easier access to a wide variety of telecommunications and network service providers. This model allows companies to retain full control over their equipment, while the colocation provider takes care of the data center management.
Container
A container is a virtualization instance able to run separate instances of an application using a single OS. More details about containerization systems and orchestrators.
CPU
A CPU or Central Processing Unit is an electronic circuit inside a computer that executes the specific instructions of every software program via basic arithmetic, logic, control and input/output operations. A CPU can be composed of several “cores”, which are the different processing cores, so that modern processors are able to perform several tasks at the same time. Additionally, every core can be able to process several threads simultaneously (Intel’s technology called “Hyperthreading”).
D
Data center
A data center or Internet data center (IDC) is a physical location where an organization or Internet service provider’s necessary computing resources are gathered. More details aboutwhat a data center is.
DataOps
DataOps, short for Data and Operations, is a methodology used by data engineers, scientists and analysts to speed up the development of applications based on Big Data, by working together with the DevOps team. It improves quality and reduces the cycle time of data analytics.
Data Sovereignty
The concept of Data Sovereignty refers to the fact that data processed by an organization is subject to the laws and regulations of the country or region where it is located. More details about this concept in this post about data protection and sovereignty in the digital economy.
DevOps
DevOps, short for Development and Operations, is a methodology based on the collaboration of IT operations and software development teams to make developmens and deployments as agile as possible. More details about the DevOps methodology.
DevSecOps
DevSecOps, short for Development, Security and Operations, is an approach that integrates the security layer from the beginning within the DevOps methodology. More details about the DevSecOps methodology.
Disaster Recovery
Disaster Recovery (DR) is a procedure to recover data and functionalities after a system has been disrupted because of a disaster — either natural or caused by humans. More details about what a Disaster Recovery plan is and how to build one.
E
Edge computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that consists of bringing data storage and computing closer to where it is generated. By moving computing capabilities closer to the source of the data, it is possible to leverage many benefits like saving bandwidth and improving response times. More details about edge computing.
F
Fault tolerance
Fault tolerance is a property that allows systems to avoid downtime. It does so by mirroring systems so that the standby system takes over without any downtime when the primary system fails. It requires complete redundancy in hardware.
G
Georedundancy
Georedundancy consists in replicating data and IT infrastructure in multiple remote data centers. Its goal is protecting data and minimizing downtime in order to guarantee normal business activity in case of an unplanned service disruption. Therefore, it is especially relevant when talking about mission-critical servers, data and applications. More details about georedundancy.
GiB
A GiB or GibiByte is a unit of measure used for data storage. A GiB is equivalent to 230 bytes (1,073,741,824 bytes).
H
HA
HA or High Availability refers to an agreed level of operational performance higher than normal period.
Hardware
The term hardware refers to the physical parts of a computer — CPU, monitor, computer data storage, graphic card, etc.
Hot migration
A hot migration is the process of moving a system or virtual machine from one server or data center to another without turning it off or disrupting its availability.
Hybrid Cloud
The Hybrid Cloud is a cloud computing deployment model that combines the dedicated resources of a Private Cloud for mission-critical applications and data with shared resources in a Public Cloud for handling unusual traffic peaks. More details about the Hybrid Cloud.
Hyperconvergence
Hyperconvergence is an IT infrastructure aiming to reduce data center complexity. Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) is a software-defined system that unifies all the elements of a traditional data center: computing, storage, networking and management. More details about hyperconvergence and HCI.
Hypervisor
A hypervisor is a layer of virtualization software that allows to create and run several virtual machines within a single server, as well as different operating systems. It is in charge of separating the resources of the virtual machine from the hardware system and of distributing them properly. It is also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM). VMware, ESXi and KVM are some examples of hypervisors. More details about hypervisors.
I
IaaS
IaaS or Infrastructure as a Service is a cloud computing service model that consists of providing and managing computing resources — such as servers, storage or networks — over the Internet. More details about what IaaS is and its advantages.
Internet Exchange Point
An Internet Exchange Point (IXP) is a physical infrastructure that makes traffic exchange easier among networks for ISPs. IXPs allow networks to interconnect directly via their infrastructure, instead of through third-party networks. More details aboutwhat an IXP is and its advantages.
IOPS
IOPS or Input/Output Operations Per Second is a unit of measurement which is used for indicating the performance of storage computing devices and network storage volumes. It’s an important information since the greater the IOPS capacity is, the greater the performance for writing or reading data is.
ISP
An ISP or Internet Service Provider is a provider of Internet services such as cloud solutions, network storage or networking.
L
Latency
The latency or network latency is the time it takes to transfer a packet between a server and an user through a network.
Legacy system
A legacy system is an old or out-of-date system, technology or software application that continues to be used by an organization because it is not possible to replace it or update it easily — or just because the organization does not wish to do so. More details about what a legacy system is.
Lift-and-shift
Lift-and-shift is a cloud migration approach that consists of moving an existing application — and its data — to a cloud infrastructure without redesigning it or applying important changes.
Load balancing
Load balancing is the process of distributing computing workloads across multiple servers. A load balancer distributes application traffic to several servers to avoid that a single application server becomes a point of failure.
M
Middleware
Middleware is a type of software used to connect software components and enterprise applications.
Monitoring
Monitoring consists of using tools to get detailed information of virtualized and physical servers, storage, network, systems, databases, platforms, etc., in order to predict problems and solve them proactively. More details about the importance of IT system monitoring.
Multicloud
The Multicloud is a cloud computing deployment model which combines cloud services from several public and private cloud providers, in order to leverage the specific advantages of multiple providers.
N
Network equipment
A network equipment or network hardware is an electronic device that allows data transfer and interaction among devices within a computers or servers network.
Network storage
Network storage is a technology that allows to share storage capacities among servers or computers through a network and remotely, thanks to a direct connection or protocols such as NFS, iSCI, etc.
NOC
A Network Operations Center (NOC) is a centralized location where an organization’s network team monitors, manages and optimizes networks, troubleshooting any network event that might arise. It is also known as “Network Management Center”. More details about Network Operations Centers.
Noisy neighbor
The concept “noisy neighbor” is an effect that happens in cloud environments and infrastructures that are shared among several customers. It occurs when the activity of a virtual machine (VM) deteriorates the performance of another VM within the same physical infrastructure. This effect is usually caused by the oversubscription of resources.
O
OPEX
OPEX, short for Operational Expenditure, refers to the amount of money a company spends on services that are necessary to keep the business running — utilities, wages, server maintenance, etc. Learn more about OPEX in this post about cloud costs.
Oversubscription
The oversubscription of resources happens when a shared hosting or Public Cloud provider offers a series of computing resources that exceeds the available capacity, because they assume customers do not use all the resources offered. More details about what oversubscription of resources is.
P
PaaS
PaaS or Platform as a Service is a cloud computing service model that provides a ready to use development environment over the Internet, in which developers can develop, manage, distribute and test their software applications. More details about PaaS or Platform as a Service.
Private Cloud
The Private Cloud is a cloud computing deployment model in which the computing resources and environment are of exclusive use by an organization. A Private Cloud is comparable to owning a data center in a company, but with the benefits of delegating its management and scaling on demand thanks to virtualization. More details about the private cloud and its advantages.
Public Cloud
The Public Cloud is a cloud computing deployment model in which an ISP offers computing resources over the Internet within an infrastructure which is shared among several organizations, based on a pay per use model. More details about the Public Cloud.
PUE
The PUE ratio (Power Usage Effectiveness) is used for measuring data centers’ energy efficiency. The PUE is the value derived from dividing the total amount of energy used by a data center facility by the energy delivered to the data center’s computing equipment. More details about the PUE ratio.
R
RAM
RAM memory or Random-Access Memory is the main memory of servers and personal devices. It temporarily stores the data of the programs in use during a session.
Refactoring
Refactoring is a cloud migration approach that consists of making some adjustment and optimization to an application so that it better fits the cloud environment.
S
SaaS
SaaS or Software as a Service is a cloud computing service model that consists of distributing cloud-hosted software applications to users over the Internet, on a subscription or purchase basis. More details about SaaS or Software as a Service.
SD-WAN
SD-WAN, short for Software-defined Wide Area Network, is a cloud-oriented approach to manage WAN networks. SD-WAN is designed to simplify and optimize branch office network connectivity. More details about SD-WAN.
Server
A server is a computer, device or computing program that manages networking and computing resources, and provides services and functionalities to other computers, programs and devices known as “clients”.
The shared-responsibility model defines that the responsibilities related to the cloud security and data protection are shared between the cloud service provider and the customer. In this model, the Internet Service Provider is responsible for the security of the cloud and the customer is responsible for the security in the cloud.
SLA
An SLA or Service-level agreement is an agreement between the service provider (ISP) and the customer which collects the specific aspects of the service in terms of quality, availability and responsibility. Inside the SLA, ISPs define the level of service of the services contracted by the customer.
Snapshot
A snapshot is a copy of the state of a system at a particular point in time.
SOC
SOC, short for Security Operations Center, is a centralized location where an organization’s security team monitors, analyzes, detects and solves any security incidents that might arise. It is also known as ISOC, short for Information Security Operations Center. More details about what a SOC is.
Software
The term software refers to the collection of computer programs and libraries (and related data) stored and run by hardware.
V
Vendor lock-in
The concept “vendor lock-in” refers to the situation of dependency on a product or service where a customer can be “stuck” when wanting to change providers, since the change entails very high costs and application compatibility issues.
Virtualization
Virtualization is the process of creating a virtual technological resource with a layer of software that separates it from the hardware or physical resource (servers, applications, networks…).
Virtual Machine
A virtual machine or VM is a virtual environment created within a physical hardware system with a hypervisor. It has its own operating system, CPU, memory, network interface and storage. The physical machine running the VM is known as the “host” and the VM emulated on that physical machine is known as the “guest”.
VPN
A VPN or Virtual Private Network is a network that allows the creation of a private, encrypted and secure connection between two points over the Internet. VPN tunnels enable sending encrypted and secure traffic. More details aboutwhat a VPN is.
Infographic of some key terms in the cloud computing field
Dutch version: Veelgebruikte begrippen van cloud computing.