Every mainstream Linux distro including Ubuntu, Fedora, openSUSE, and Arch uses systemd by default.
But there are many non-systemd distros like Void Linux that uses lightweight runit for better performance or Devuan that uses sysvinit on principal basis.
The problem comes when you are trying to follow some tutorial or documentation and it has commands specific to systemd or some other init service.
And this is where you have to check if your Linux system uses systemd or something else.
One way would to be check the process with PID 1 (after all, an init system is the first process to run on a Linux system).
ps 1But its output could be misleading as often it shows /sbin/init which is just a soft link to actual init process.
If you follow that symbolic link, you can get the init system information. There are two ways of doing that:
- Using the stat command
- Using the readlink command
So let’s start with the first one.
📋
These methods were tested with 6 init systems: Systemd, OpenRC, SysVnint, Busybox, runit, and s6.
Method 1: Check if systemd is in use with the stat command
Here’s how you can use the stat command to find out what init system you are using:
stat /sbin/initIf you are using a systemd-powered distro, then it will show you the following output:
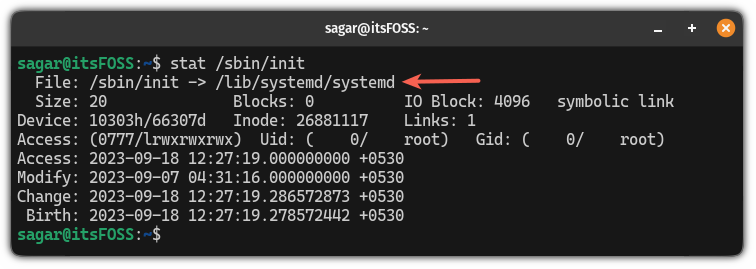
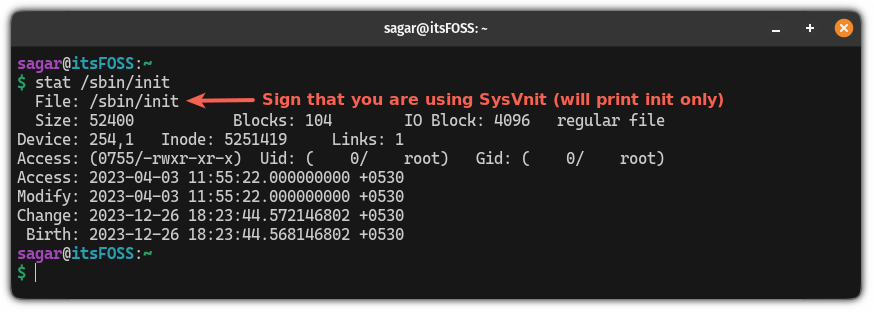
But if you are using anything else than systemd, it will show the init name unless you are using SysVnit which will only show you init instead of sysvnit:
Method 2: Check the init system using the readlink command
Unlike the previous method, when you use the readlink command, it will only print the name of the init system.
So if you want to know if you are using Systemd or not, simply use the following command:
readlink /sbin/init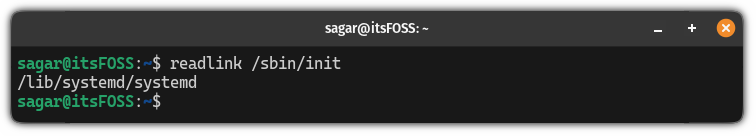
If you are using the OpenRC init service, then it will show the following output:
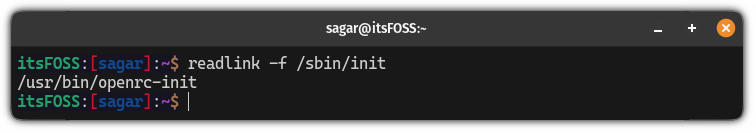
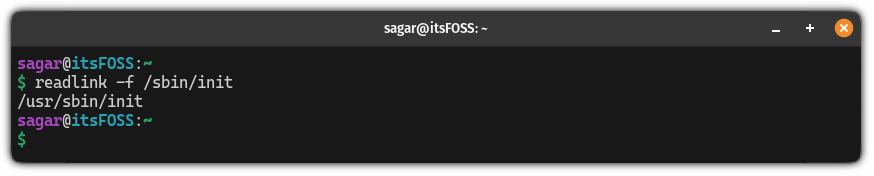
But if you are using SysVnit, then, it will show you the following output:
Tiny ‘script’ I wrote for you
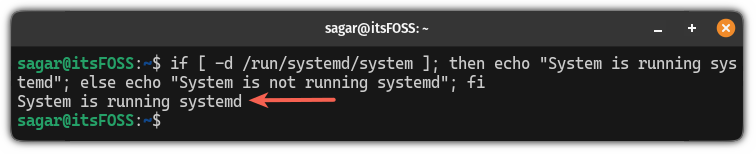
Another way is to check if the /run/systemd/system directory exists or not.
Well, the easiest way to find out is to use an if-else bash command in your terminal which will check if you are running a systemd-powered distro or not:
if [ -d /run/systemd/system ]; then echo "System is running systemd"; else echo "System is not running systemd"; fi
More on systemd
Once you know you are using the systemd-powered distro, here’s how you can manage services using the systemctl command:

Want to create a systemd service from scratch? You can do that too:

I hope you will find this guide helpful.