Before going to the program first let us see what is Factorial of a Number? and what is Recursion?
Factorial of a Number:
The factorial of a Number n, denoted by n! , is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n.
The value of 0! is 1 according to the convention for an empty product.
For example,
6! = 6 * 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1 = 720
Recursion:
In C programming language, if a function calls itself over and over again then that function is known as Recursive Function.
The process of function calling itself repeatedly is known as Recursion.
Related: Factorial of a Number in C++ without using Recursion
Program code for Factorial of a Number using Recursion:
/* Factorial of a number using Recursion */
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h> int fact(int); void main()
{ int num,f; clrscr(); cout<<"n Enter the number: "; cin>>num; f=fact(num); cout<<"n The factorial of " <<num<<" is "<<f; getch();
} int fact(int n)
{ if(n==0||n==1) return 1; else return(n * fact(n-1));
}
Related: Factorial of a Number in C using Recursion
Working:
- First the computer reads the number to find the factorial of the number from the user.
- Then using recursive function the factorial value is calculated and returns the factorial value to main function.
- Finally the factorial value of the given number is printed.
Step by Step working of the above Program Code:
Let us assume that the number entered by the user is 5.
- It assigns the value of n=5.
- Then using a variable f the recursive function fact(n) is called.
2.1. n==0 || n==1 (5==0 || 5==1) if condition is false.
So it goes to the else part.
else
return(n * fact(n-1)) So, (return(5 * fact(4))) // function calls itself
2.2. n==0 || n==1 (4==0 || 4==1) if condition is false.
So it goes to the else part.
else
return(n * fact(n-1)) So, (return(4 * fact(3))) // function calls itself
2.3. n==0 || n==1 (3==0 || 3==1) if condition is false.
So it goes to the else part.
else
return(n * fact(n-1)) So, (return(3 * fact(2))) // function calls itself
2.4. n==0 || n==1 (2==0 || 2==1) if condition is false.
So it goes to the else part.
else
return(n * fact(n-1)) So, (return(2 * fact(1))) // function calls itself
2.5. n==0 || n==1 (1==0 || 1==1) if condition is true.
So it return the value 1 to fact(1) in step 2.4.
which further return the value 2 to fact(2) in step 2.3.
which further return the value 6 to fact(3) in step 2.2.
which further return the value 24 to fact(4) in step 2.1.
which further return the value 120 to f in main function.
- Finally it prints as given below
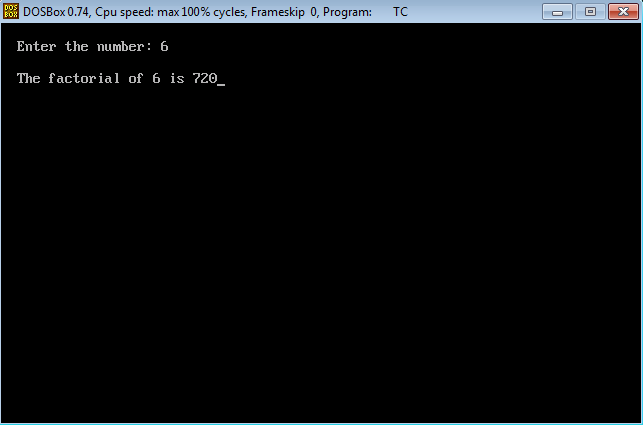
The Factorial of 5 is 120
- Thus the program execution is completed.
Output: