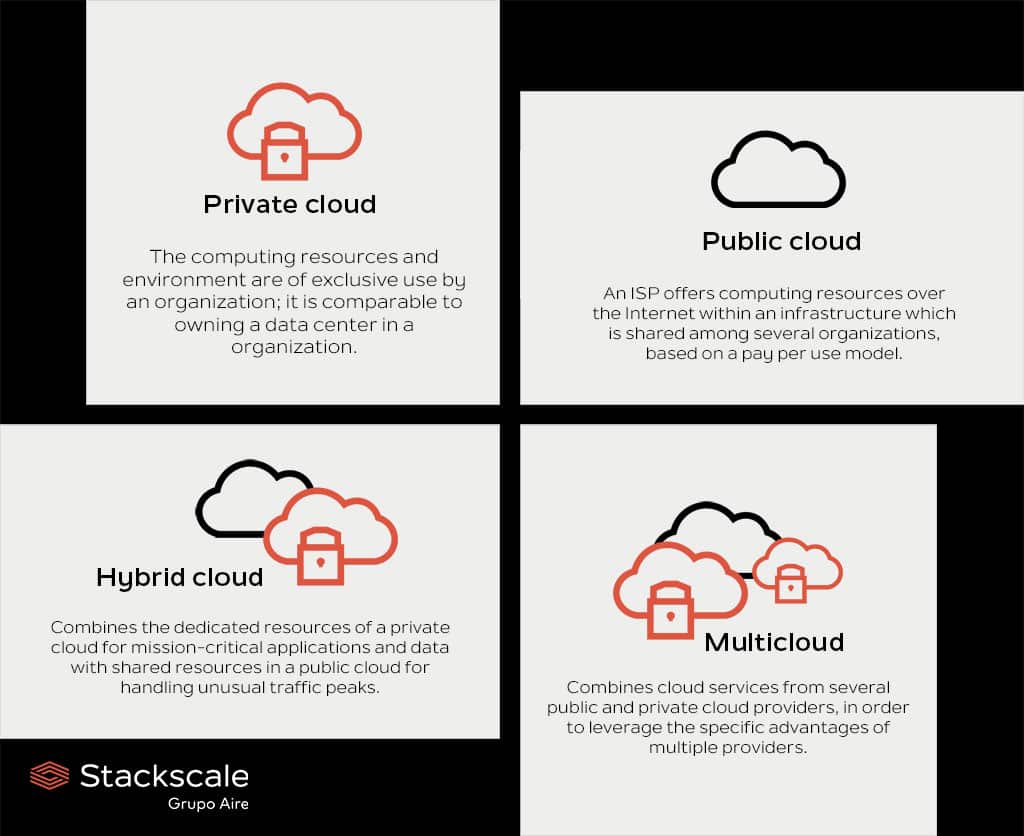
There are 4 main types of cloud computing: private cloud, public cloud, hybrid cloud and multicloud. Each of these cloud deployment models offers different features and advantages. Therefore, the right model for each company will depend on their real needs and goals.
Having a virtualized data center provides a lot of benefits to organizations, but not all solutions are made the same. In fact, two cloud solutions, even if they belong to the same type, are not the same either. Diverse aspects must be considered when choosing the right type of cloud for a project, including performance, costs, security and so on.
Private cloud
The private cloud is a cloud computing deployment model in which the environment and computing resources are exclusively dedicated to a single customer. As a single-tenant infrastructure, it is comparable to owning a data center in a company, but it allows scaling services on demand thanks to virtualization.
The concept “cloud datacenter” is often used to refer to the private cloud as well.
Private cloud solutions offer greater security and control to companies, as they do not have to share their resources with other customers. As a result, cloud performance is not affected by the activities of noisy neighbors. Besides, by relying on a specialized private cloud provider, companies can completely forget about the management of physical servers.
Originally, private cloud environments used to be hosted in on-premises data centers within the company’s facilities, but this is less and less common. Why? Because opting for a hosted private cloud in a specialized data center provides much more value and advantages to companies.
Types of Private Cloud
There are different types of private cloud that offer different advantages to businesses:
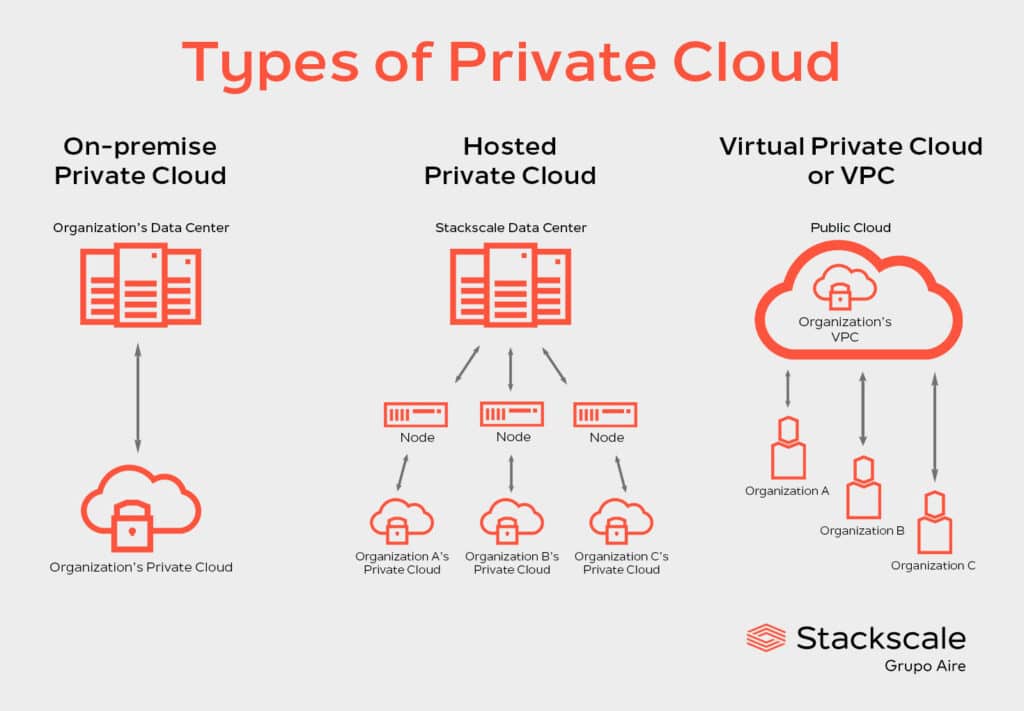

- On-premise Private Cloud. This type of Private Cloud consists of creating a private, virtualized environment within the organization’s on-premise data center.
- Hosted Private Cloud. This type of Private Cloud offers dedicated resources to organizations, delivered by a third-party provider such as Stackscale. Servers continue to be exclusive to each organization and independent from the activities of other customers.
- Virtual Private Cloud or VPC. This type of Private Cloud uses an isolated environment within a Public Cloud. This allows organizations to run their workloads using private resources but the servers continue to be shared with other customers.
Private cloud costs
Unlike some companies might think, a private cloud is not necessarily more expensive than a public cloud. In fact, since most business workloads are predictable, it is often more cost-efficient to run them in a private cloud.
Private cloud solutions allow businesses to remove big initial investments in equipment acquisition (CAPEX) as well as reduce management costs (OPEX). All that without giving up the advantages of having dedicated computing resources. Moreover, as providers are in charge of guaranteeing the technological evolution of the infrastructure, companies do not need to cover that cost overrun.
At Stackscale we debunk the myth of expensive private clouds by offering truly competitive private cloud solutions. We design and develop high-performance private cloud environments so that companies do not need to invest a lot of money on hardware.
Private cloud use cases
Private cloud environments are ideal for all kinds of organizations and projects, including:
- corporate applications,
- public administrations,
- IT services providers,
- high-traffic websites, etc.
A private cloud solution is particularly suitable for use cases where high performance, regulatory compliance and cost optimization are essential. Furthermore, private cloud is the most common cloud deployment model to host mission-critical data and applications.
Public cloud
The public cloud is a cloud computing deployment model in which a cloud service provider offers resources over the Internet with a pay-per-use model. It is a multi-tenant model. Each customer has a virtual computing environment separated from other users within an infrastructure shared among multiple customers. This can negatively affect performance due to the activities of other neighboring users, when resources are oversubscribed by the cloud provider.
The public cloud deployment model is known for being extremely flexible and scalable, which makes it a good choice for handling peak loads. However, despite what people might think, it isn’t always the most economical cloud solution.
Public cloud costs
The public cloud’s pay-per-use model, which enables companies to only pay for the resources they use, usually involves considerable savings during the initial phases of a project. However, this economic advantage tends to disappear as the platform evolves. Oversubscription limits the control over the resources and, as a consequence, over cloud costs. Fast provisioning and lack of visibility and control can lead to contracting more resources than necessary.
“Cost management must be approached differently when moving off-premises. Fast provisioning in the cloud must be properly managed to keep control of costs over time.”
As projects grow, it is easy for public cloud costs to become hard to control and businesses can incur unnecessary expenses. So, in projects hosted in public cloud environments, it is very important to carefully keep control of the contracted resources. Not only to optimize costs, but also to keep them under control.
Public cloud use cases
Public cloud can be a good starting point for small projects and startups, since it can be deployed very quickly. However, as we mentioned before, as the company and project grow, the expenses run the risk of going through the roof. That is why more and more companies opt for combining private cloud and public cloud environments to leverage the advantages of both models, as we explain below.
Hybrid cloud
The hybrid cloud is a cloud deployment model which combines private computing resources and public computing resources. An example of hybrid cloud infrastructure can be the combination of a private cloud for ensuring high performance, security and control for mission-critical applications and data, and a public cloud for maximum scalability to handle unusual traffic peaks.
So, this hybrid model combines the advantages of both private and public cloud environments to provide additional flexibility to companies. The key to a good hybrid cloud is guaranteeing a good interoperability between both environments, so that its management is agile and efficient. These are some of the elements it is important to control because they can be critical in an hybrid cloud environment:
- Security: the data transfer flow must be controlled with encryption solutions and VPNs. At Stackscale we offer solutions to interconnect the infrastructure and private cloud solutions of our clients with public cloud solutions such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud.
- Hypervisor: it is possible that the private cloud and the public cloud hypervisors are different. Therefore, it is necessary to use a solution to simplify the interoperability between both of them.
- Vision of the platform and service: it is necessary to have a clear vision of how the infrastructure is deployed in one or several data centers. For doing so, companies can develop solutions, via API, to control it or use some third-party software that makes the management easier.
Hybrid cloud costs
Hybrid cloud environments can help companies optimize costs, since they allow to place different applications and workloads in the optimal cloud environment for each of them. Nevertheless, it is essential to properly design, deploy and manage the environment in order to avoid unnecessary expenses. Understanding and monitoring cloud costs at a global level is especially important when opting for a hybrid cloud infrastructure.
To make cost management easier, choosing a provider that offers transparent billing can be very helpful. In this regard, at Stackscale we offer a simplified pricing and billing policy that allows customers to know their infrastructure costs beforehand. This enables them to control their cloud environment costs without the need for complex calculations or formulas and without surprises at the end of the month.
Hybrid cloud use cases
Hybrid cloud can be an useful option for companies that need an infrastructure based on the private cloud, for greater control over the infrastructure in terms of costs and resources, but that occasionally need to overflow services in a public cloud platform.
Multicloud
Multicloud is a cloud deployment model which combines multiple cloud services — both private and public — from several cloud service providers. This cloud computing deployment model allows to combine the benefits of different types of cloud with the specific advantages of several service providers.
A multicloud infrastructure can be composed, for instance, of 2 private cloud environments and 1 public cloud environment. One of the cloud solutions can be used, for example, as an infrastructure reserved for Disaster Recovery. In addition, by combining different regional cloud providers, companies can operate closer to their customers. This can be helpful for reducing latency, complying with data protection and sovereignty regulations, etc.
This type of cloud offers an additional level of flexibility and it is likely to become more common over time. It not only helps reduce dependance in a single provider but also reinforce digital transformation processes. However, as a complex cloud solution, it demands a great level of management and security which is not accessible to all companies.
Multicloud costs
Just like hybrid cloud environments, multicloud environments can help companies optimize costs by choosing the most appropriate cloud solution for each workload and application. Nevertheless, it also requires proper cost visibility and management in order to avoid overspending. Understanding and monitoring cloud costs at a global level is especially important when opting for a multicloud infrastructure.
Multicloud use cases
Although suitable for a large variety of use cases, multicloud infrastructures are especially deployed in big and complex projects that also require complex solutions. But, as mentioned above, it is likely to become more commonly used over time.
Brief comparison of types of cloud computing

As we have seen, every cloud computing type offers different features and advantages, and the best option will depend on the needs of each particular company.
| Cloud computing type | Main features and benefits | ||
| Private cloud |
|
||
| Public cloud |
|
||
| Hybrid cloud |
|
||
| Multicloud |
|
||
Looking for a cloud solution adapted to your business?
Tell us about your project and we will help you find a solution that adapts to your needs.